Yves here. The text of a tweet from Thomas Keith (if you have a Twitter account, please follow him!) summarizes estimates of the many substantial hard dollar costs Israel incurred in its Iran misadventure, also with economic losses that have a much longer tail, such as the loss of venture capital, since no investor with an operating brain cell wants to operate out of a conflict zone. As most readers know, a significant majority of experts and other commentators see the cessation of hostilities as temporary and expect more kinetic action, as in more destruction.
We said at the outset that Israel has a glass jaw. It’s never been on the receiving end of the punishment it has been casually handing out for decades. As Alastair Crooke said after the October 7 attack, the raison d’etre for Israel was to be a safe haven for Jews. That belief was damaged then and not it has been smashed to bits.
Official tallies seem modest compared to the Keith’s list:
Israel estimates indicate that the cost may rise to $20 billion, with damage affecting the economy, society, and strategic infrastructure.
The Compensation Fund of the Israeli Tax Authority stated that it had received around 39,000 claims for direct material damage resulting…
— Elijah J. Magnier 🇪🇺 (@ejmalrai) June 26, 2025
Two days earlier, the Times of Israel estimated the damage at a paltry $1.5 billion, only twice the level of damage inflicted in the Hamas attacks. For reference, Israel’s GDP is $513 billion.
Note that even though the list below is extensive and specific, there are further costs it omits, in part because they can’t yet be reasonably estimated:
1. The severe economic downdraft as more Israelis flee if and when the country is opened up again, particularly the high-skilled ones on whom the economy depends. We covered that vulnerability at length in a June 2024 post, Israel Economy Bleeding Out as Damage Compounds. Note in particular that it cited an Israeli economist who says the country depends on a mere 300,000 professionals1
2. The loss of more IDF soldiers, which Israel has yet to admit to.
3. The cost of the damage to ports, which goes beyond the cost of repairing infrastructure to the loss of shipments, which could be protracted if insurers are leery
4. The odds that the BDS movement will gain more steam as Israel kept up its genocide even during the Iran conflict. From Aljazeera:
Since Israel began attacking Iran on June 13, global attention on the plight of Palestinians in the occupied territory has faded from the headlines.
But Israel has continued to attack Palestinians in Gaza, while conducting deadly raids in the West Bank…
“Israel is using the diverted attention away from Gaza to continue to carry out atrocious crimes against starving civilians,” said Omar Rahman, an expert on Israel and Palestine for the Middle East Council on Global Affairs think tank.
“We have also seen a lot of military and settler activity in the West Bank in recent days,” he told Al Jazeera.
Israel’s violence against helpless Palestinians at the GHF site on Tuesday resulted in the highest single death toll at any GHF site since the controversial organisation began operations last month. It has been lambasted for what opponents have called the militarisation of humanitarian aid relief.
Readers can add to this and Thomas Keith’s list; full text below the embed:
Israel entered the 12-day exchange convinced it could absorb costs; the ledger now shows a nation bleeding cash, talent, and confidence. Direct military outlays hit $5 B in the first week, then ballooned to $725 M every 24 hours, $593 M on offensive strikes that failed to silence…
— Thomas Keith (@iwasnevrhere_) June 25, 2025
Israel entered the 12-day exchange convinced it could absorb costs; the ledger now shows a nation bleeding cash, talent, and confidence. Direct military outlays hit $5 B in the first week, then ballooned to $725 M every 24 hours, $593 M on offensive strikes that failed to silence Iran, $132 M on frantic mobilisation and missile intercepts that still let 400 warheads through. Iron Dome batteries alone inhaled $10 M to $200 M per day while Iranian salvos sailed past them and erased $1.47 B in civilian property, triggering 38 700 damage claims, 11 000 evacuations, and 30 condemned high-rise skeletons across Tel Aviv’s financial spine.
The Weizmann Institute, Israel’s prestige export, lies in shards, 45 labs gone and $500 M in biomedical IP incinerated, pulling decades of grant pipelines and pharma partnerships off the table overnight. Intel’s Kiryat Gat fabs froze mid-wafer, choking a supply chain that feeds 64 % of Israel’s exports and 1/5 of its GDP; the high-tech sector now runs on skeleton crews because 300 000 reservists were yanked from R&D floors and data centers to guard empty runways at Tel Nof. Commercial flights halted twice at Ben Gurion, insurers jacked premiums, and foreign airlines rerouted around a country that once sold itself as the region’s safe hub.
Capital is already in flight. More than 80 000 Israelis emigrated in 2024, the largest outflow since 1948, pushing the two-year total above 500 000 and forcing Netanyahu’s cabinet to slap a travel ban on Jewish dual nationals to stem the leak. Investor confidence cratered: venture funds paused term sheets, construction sites stand idle, and mega-projects wait on credit that no longer clears. The finance ministry, staring at a deficit set to shove public debt past 75 % of GDP, begged for an extra $857 M in defence cash while slicing $200 M from hospitals and schools.
Analysts peg Israel’s aggregate loss between $11.5 B and $17.8 B, up to 3.3 % of GDP, before counting long-tail hits from halted exports, cancelled IPOs, and sovereign-risk downgrades. Iran, still sitting on its uranium stockpile, spent a fraction of that yet forced the self-styled “Start-Up Nation” into a liquidity scramble, an insurance panic, and a brain-drain spiral. Tel Aviv promised deterrence; Tehran handed it a balance sheet in red ink and the visible stamp of strategic humiliation.
_____
1
It’s not clear how much depth and resilience Israel’s economy (and society) have. Some on the anti-war right assert that Israel is a fake economy, more an imperial outpost than a reasonably self-supporting country. This is a topic I’d like to examine further but lack the bandwidth at this juncture. Any reader data points (better yet data sources) are very much welcome.
On the surface, Israel’s import and export statistics don’t indicate much US dependence…
To flip the question: what becomes of Israel if it continues to suffer an exodus, particularly of highly skilled, highly mobile professionals and experts? Many argue that the US and wealthy Zionists can continue to prop Israel up on an open-ended basis. But what if enough “talent” leaves and businesses shutter so that the support goes into what increasingly looks like a welfare queen? And how does a state that has become that much of a dependency defend itself in a neighborhood that it has united against it?
Now to some of the highlights from the important Mondoweiss story, which I encourage you to read in full. Critically, it describes severe, potentially irreparable damage all across the economy:
The economic indicators speak of nothing less than an economic catastrophe. Over 46,000 businesses have gone bankrupt, tourism has stopped, Israel’s credit rating was lowered, Israeli bonds are sold at the prices of almost “junk bonds” levels, and the foreign investments that have already dropped by 60% in the first quarter of 2023 (as a result of the policies of Israel’s far-right government before October 7) show no prospects of recovery. The majority of the money invested in Israeli investment funds was diverted to investments abroad because Israelis do not want their own pension funds and insurance funds or their own savings to be tied to the fate of the State of Israel. This has caused a surprising stability in the Israeli stock market because funds invested in foreign stocks and bonds generated profit in foreign currency, which was multiplied by the rise in the exchange rate between foreign currencies and the Israeli Shekel. But then Intel scuttled a $25 billion investment plan in Israel, the biggest BDS victory ever.
The crisis strikes deeper at the means of production of the Israeli economy.
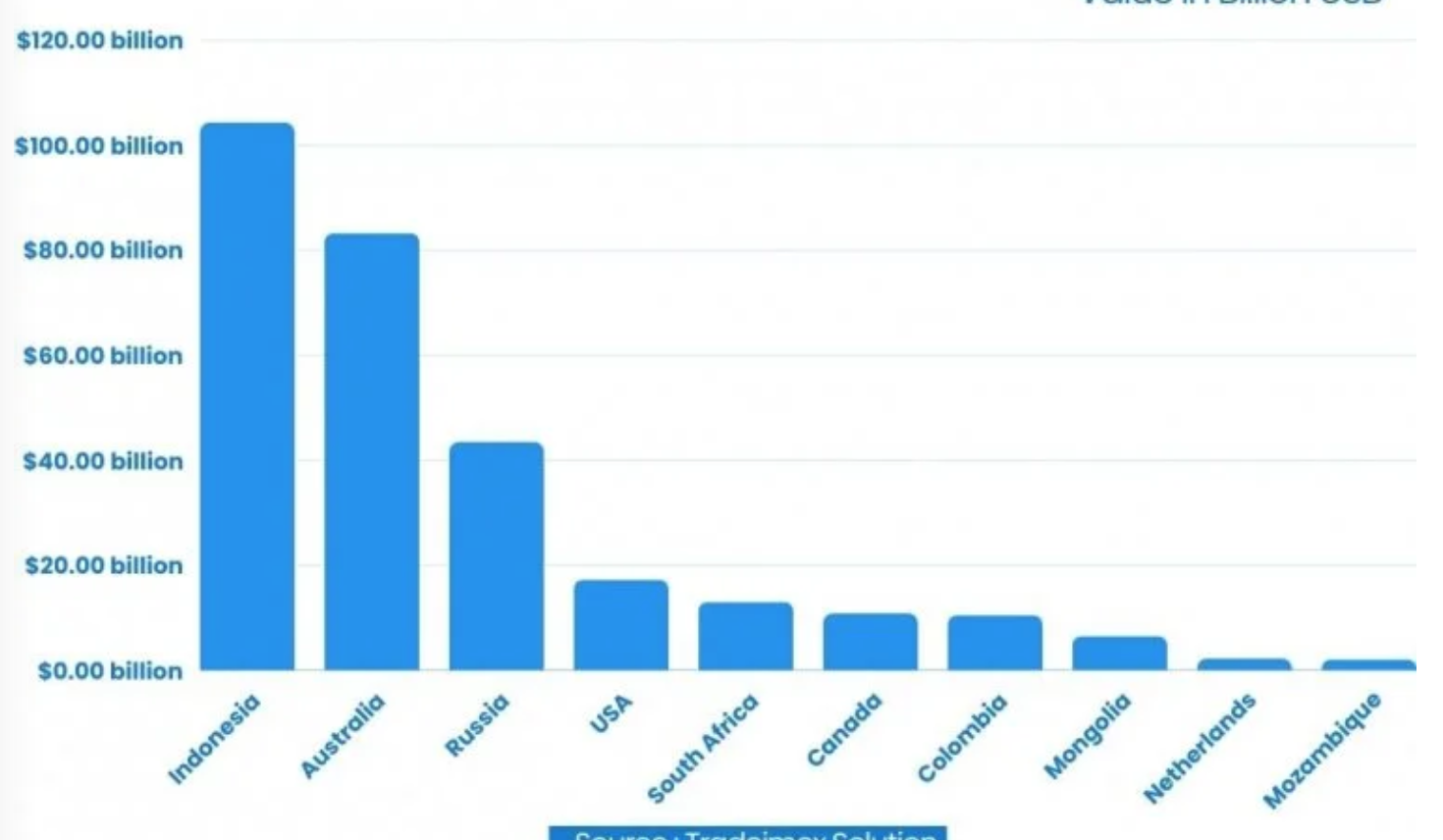
These are all financial indicators. But the crisis strikes deeper at the means of production of the Israeli economy. Israel’s power grid, which has largely switched to natural gas, still depends on coal to supply demand. The biggest supplier of coal to Israel is Colombia, which announced that it would suspend coal shipments to Israel as long as the genocide was ongoing. After Colombia, the next two biggest suppliers are South Africa and Russia. Without reliable and continuous electricity, Israel will no longer be able to pretend to be a developed economy. Server farms do not work without 24-hour power, and no one knows how many blackouts the Israeli high-tech sector could potentially survive. International tech companies have already started closing their branches in Israel.An aside: the loss of Colombia’s coal supplies clearly would have a serious impact, if nothing else on prices as Israel scrambles for substitute sources. Whether the result is Ukraine-style daily outages has yet to be seen, but if so, for an advanced economy, the impact would be devastating. These are the top coal exporters in 2023, per Tradeimex Solutions, so Israel is not bereft of alternatives.
But how quickly can it line up replacement supply agreements? And to what extent would these new shipments be vulnerable to Houthi attacks?
The flip side is this section may somewhat understate the deteriorating condition of Israel’s businesses. In a July story, the Cradle cites CEO of Israeli information services and credit risk management firm, CofaceBdi, who said 60,000 businesses are expected to have closed by year end 2024. The tweeted video below claims (without sourcing, but its other stats echo those from mainstream accounts) that 50% of startups are on track to closing within six months:
Israel’s Economy is falling apart from so many angles pic.twitter.com/2iPeLPipyB
— Gaza Under Attack_🇵🇸 (@Palestine001_) July 17, 2024
Back to Mondoweiss:
Israel’s reputation as a “startup nation” depends on its tech sector, which in turn depends on highly educated employees. Israeli academics report that joint research with universities abroad has declined sharply thanks to the efforts of student encampments. Israeli newspapers are full of articles about the exodus of educated Israelis. Prof. Dan Ben David, a famous economist, argued that the Israeli economy is held together by 300,000 people (the senior staff in universities, tech companies, and hospitals). Once a significant portion of these people leaves, he says, “We won’t become a third world country, we just won’t be anymore.”…
The two sectors of the Israeli economy that do not report a crash are the arms companies, which are reporting high sales (although most of them are domestic, arming the genocide), and the “exits” — as international corporations scavenge the carcasses of Israel’s tech sector looking for bargains. Even Google expressed interest in buying the Israeli cyber security company Wiz, founded by Israeli intelligence officers who are eager to sell their company to Google in order to be able to leave Israel…
In the age of the information economy, the economic prospects of states are neither determined by raw materials nor the quality of the workforce. Instead, we live in an era of an “economy of expectations.” The hype of Israel’s “startup nation” has turned into a #Shutdownnation. Two senior Israeli economists, Jugene Kendel and Ron Tzur, published a secret report in which they predict that Israel will not survive to its 100th year. The report is kept secret because they do not want it to become a self-fulfilling prophecy, but they gave interviews about it.